AGENTiGraph An Interactive Knowledge Graph Platform for LLM-based Chatbots utilizing Private Data
A summary of the paper (link in resources section).
What this paper is about
The core problem
LLMs, while powerful, face several challenges:
- Hallucination, especially in complex scenarios
- Limited reasoning abilities
- Factual inconsistencies
- Difficulty with domain-specific tasks
AGENTiGraph addresses these issues by grounding LLM responses in structured knowledge graphs, providing a foundation for more accurate and reliable information retrieval and reasoning.
The Solution: Multi-Agent Architecture
AGENTiGraph employs a multi-agent system where each agent specializes in a specific task:
- User Intent Interpretation Agent
- Interprets natural language input
- Determines underlying user intent
- Uses Few-Shot Learning and Chain-of-Thought reasoning
- Key Concept Extraction Agent
- Performs Named Entity Recognition
- Extracts relationships between concepts
- Maps concepts to knowledge graph entities
- Task Planning Agent
- Decomposes intent into executable tasks
- Creates logical task sequences
- Optimizes execution order
- Knowledge Graph Interaction Agent
- Translates tasks into graph queries
- Manages database interactions
- Adapts queries based on results
- Reasoning Agent
- Applies logical inference to query results
- Enhances raw data with contextual understanding
- Bridges structured and unstructured knowledge
- Response Generation Agent
- Synthesizes information into coherent responses
- Ensures alignment with query context
- Balances technical accuracy with comprehensibility
- Dynamic Knowledge Integration Agent
- Updates knowledge graph with new information
- Manages knowledge integration
- Ensures data consistency
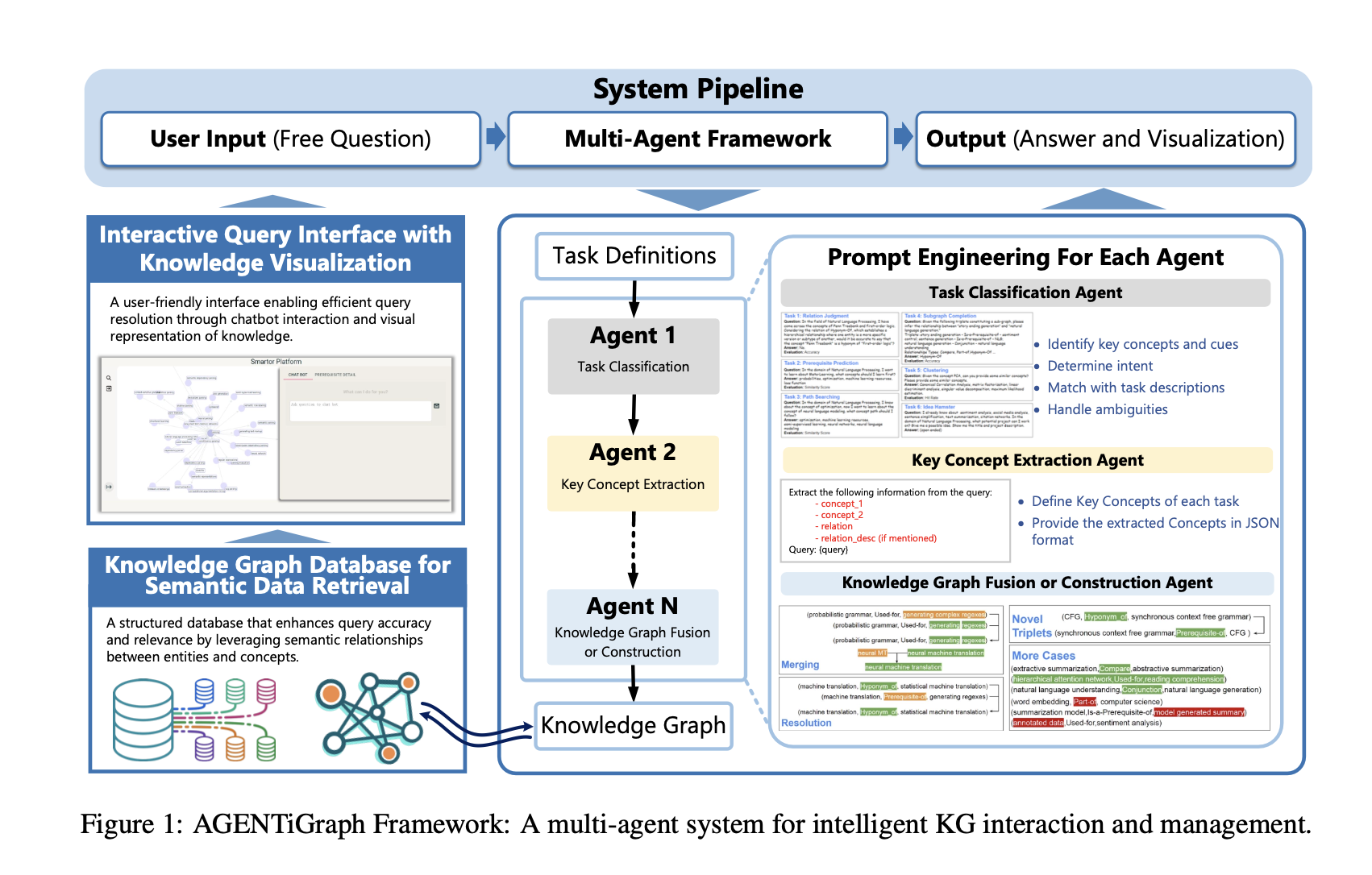
What are the differences between the agents
The only differences between the agents is the system prompt given to each agent. All agents use the same underlying LLM. No special training or fine tuning is performed.
How do the agents interact with each other and the KG
The agents work in a sequential pipeline, where:
- Each agent processes the output of the previous agent
- The Knowledge Graph serves as a central truth source
- Continuous updates maintain knowledge freshness
- Real-time visualization helps users understand relationships
The Dynamic Knowledge Integration Agent is prompted to interface with the Neo4j db using LLM-generated Cypher queries (see Appendix A.7).
Framework evaluation methodology
AGENTiGraph’s performance was evaluated by generating a dataset and then evaluating performance based on that dataset.
Dataset Generation:
- 3,500 test cases
- Six predefined task types plus free-form queries
- Generated using LLMs and verified by humans
Performance Metrics:
- 95.12% accuracy in task classification: correctly classify a question as a type of task where the tasks are defined by the paper (6 categories + 1 free form). An F1 score is also calculated which calculates ascore taking into account precision and recall.
- 90.45% success rate in task execution (the paper doesn’t detail how execution success was determined)
Note that AgentiGraph performs better than standalone llms although the gap narrows between AgentiGraph and larger llms.
Follow up areas to explore
- Alternative Architectures
- Comparison with other multi-agent systems
- Integration with newer LLM architectures
- Exploration of different knowledge graph structures
- Advanced Reasoning
- Enhancement of multi-hop reasoning capabilities
- Improvement of chain-of-thought processes
- Development of more sophisticated inference methods
- few shot learning (and other prompt engineering techniques)
-
F1 evaluation with precision and recall
- RAG Evolution
- Comparison with Retrieval-Augmented Generation
- Integration with large context windows
- Hybrid approaches combining RAG and knowledge graphs